Mesothelioma (Asbestos) Cancer facts
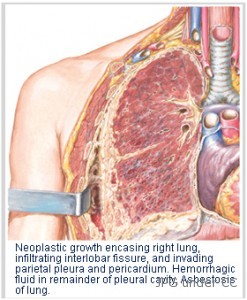
Asbestos Cancer Overview
Mesothelioma (or asbestos cancer) is a rare kind of cancer that is almost solely caused by exposure to asbestos. With this disease, the cells known as mesothelium are affected and become malignant. These cells are the chest and abdominal cavities’ protective lining. It covers most of the internal organs of the body aside from the two cavities mentioned like the heart and lungs.
Those with this disease have inhaled asbestos particles in their workplace or must have been exposed to asbestos fibers and dust even in their own homes. By simply washing the clothes of someone who has been exposed to asbestos may also put him in the same risk.
TYPES AND FORMS
- Pleural Mesothelioma – a type of mesothelioma cancer wherein there is a fluid build up in the pleural or chest cavity.
- Peritoneal Mesothelioma – a type of mesothelioma cancer wherein there is fluid accumulation in the abdominal cavity.
SYMPTOMS
Sadly, mesothelioma symptoms may only start to appear after twenty to fifty years from the time the person was exposed to asbestos. The most common symptoms are cough, chest pain and shortness of breath. If the chest pains are the result of fluid accumulation in the pleural space, then more likely what the person has is pleural mesothelioma.
For peritoneal mesothelioma, the symptoms are pain and swelling of the abdomen due to the fluid build up in the abdominal cavity, weight loss, abnormal blood clotting, anemia, bowel obstruction and fever. Once the cancer has already spread, symptoms such as neck and face swelling may be observed as well as pain in swallowing.
The other symptoms and signs that may be noticed that affect the pleura are fluid build up in the area surrounding the lungs, pain in the chest wall, fatigue, coughing of blood, wheezing or hoarse cough, and shortness of breath. In cases where there are already several tumor masses, a collapsed lung may be developed. It may even spread to other parts of the body. The tumors in the abdominal cavity regions are commonly late when showing symptoms, e.g., abdominal pain, abdominal mass, jaundice, severe ascites, blood clot in the lung’s arteries, low blood sugar level and bleeding of organs.
DIAGNOSIS
Diagnosing mesothelioma requires a careful assessment of both radiological and clinical findings. In addition, a biopsy of the tumor is often used to confirm the diagnosis. The physician will likely review the patient’s history (including exposure to asbestos) and perform various examinations and tests such as x-rays and lung function tests on the patient. An MRI or CT scan may also be performed as well.
RISK FACTORS AND CAUSES
Mesothelioma is relatively rare in nature but nevertheless increasing in number. In Western nations that are highly industrialized, the malignant mesothelioma victims range from 7 to 40 per 1 million depending on the population’s asbestos exposure. In 2004, the incident of this cancer is 15 for every 1 million Americans. Men are more prone to this type of cancer than women, with risk increasing with age. However, it may appear in either gender regardless of age.
There is a high risk of getting this disease if the individual’s working environment continuously exposes him to asbestos. All cases of mesothelioma have a history of asbestos exposure except for a very few. Asbestos is a form of mineral that occurs when strong fibers are separated into thin woven or threads. Asbestos is actually used in a number of industrial products such as roof shingles, textiles, insulations, cement, flooring products and brake linings.
Tiny particles of asbestos floating in the air, if inhaled, may result into serious health problems and even to mesothelioma. In a few rare cases, this disease was also associated with the inhalation of erionite (a fibrous silicate), with irradiation and with Thorotrast.
Asbestos may also lead to lung cancer and other lung illnesses and ailments. Smoking, though not really attributable to mesothelioma, may increase the person’s risk to mesothelioma if combines with asbestos exposure. A virus called SV40 or virus 40 is observed to be a co-factor in mesothelioma development.
TREATMENT
Just like with other types of cancers, treatment is highly dependent on the time of diagnosis. Cancers diagnosed at the late stages are usually impossible to cure already. Another factor is the location of the tumor. Usual mesothelioma cases are treated with a combination of surgery, radiation and chemotherapy. Surgery is mainly done to remove the cancer as well as the build up of fluid either in the pleural cavity or the abdominal cavity of the patient.
Radiation is done to kill the cancer cells with the use of high-energy X-rays. Chemotherapy is actually the drugs that kill the cancer cells. Other means of curing mesothelioma are immunotherapy, treatment by stages and through the heated intraoperative intraperitoneal chemotherapy. For advanced stages, treatments such as paracentesis and thoracentesis may be done to minimize discomfort.
Currently, more approaches to treating this disease are being evaluated mainly because many patients fail to responds to the currently available treatments as well as the undesirable side effects they have. In fact, a new drug is being considered, as reported by the American Society of Clinical Oncology, to show good results in curing mesothelioma. This drug is names Alimta with cisplatin. Still, more drugs are being tested to cure asbestos cancer.
