Gallbladder Cancer facts
OVERVIEW
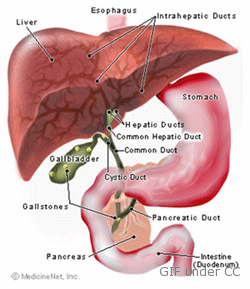
The gallbladder is a small sac found on the right base of the liver. This small muscular pouch is the one responsible in storing the fluids secreted by the liver for the completion of the entire digestion process. Gallbladder cancer is a rare kind of disease that is mostly seen on very old people ages 70 years and up. Old women are known to be the most affected than men.
The cancer of the gallbladder is not easily detected and hardly ever yields indications in its primary stages. In most cases, patients only recognized that they have this growth the time when gallbladder is removed for medication and treatment of gallstones. That is the reason why the moment it is discovered, to a certain extent, the cancer has already progressed. If the disease is detected at an early stage, removing the gallbladder and part of the bile duct, both of which are known as biliary system is taken out to thwart the spread of cancer cells.
Those who have severe cases of gallbladder disease are provided with various advanced treatments to alleviate further complications and somehow recuperate and enhance the lives of gallbladder disease sufferers.
TYPES AND FORMS
There are seven types of Gallbladder cancer. This disease has several kinds as the gallbladder has a lot of different types of cells.
- Adenocarcinoma – This is considered as the most common kind of gallbladder cancer due to its origin. If the cancer originates in the gland cells producing thick mucus in the facing of the gallbladder, this type of cancer is known as adenocarcinoma. There are three kinds of adenocarcinoma cancer of the gallbladder:
- Non Papillary adenocarcinoma
- Papillary adenocarcinoma
- Mucinous adenocarcinoma
- Squamous Cell Cancer of the Gallbladder – This is similar with adenocarcinoma; the only difference is that it doesn’t form in the gland cells. This type of cancer in the gallbladder is formed in the skin-like cells developed in the inside layer of the gallbladder.
- Adenosquamous Cell Cancer of the Gallbladder – This type of cancer is also called by medical professionals as ‘mixed histology’. This is a combination of the Squamous and Glandular cancer cells of the gallbladder. The treatment for Adenosquamous is similar with that of the Adenocarcinoma.
- Small Cell Cancer of the Gallbladder – This type of cancer cells is known as ‘oat cell carcinoma’ due to its oat-like shape.
- Sarcoma of the Gallbladder – In this type of cancer of the gallbladder, the connective tissues are affected. This means that the protective layers and tissues in the body such as the blood vessels, muscles and nerves are greatly involved. Apart from this, the cancer is known as sarcoma the moment cancerous cells originated in the muscle region.
- Neuroendocrine Tumor of the Gallbladder – This type of cancer is very uncommon and they are mostly found in the digestive region or hormone producing tissues.
- Lymphoma and Melanoma of the Gallbladder – This is the rarest type of gallbladder cancer. Base on research, there are only 10 to 20 people in the world who are diagnosed with this kind of disease, enough to explicate the rarity. This type of cancer is not curable by surgery, so patients are suggested to undergo chemotherapy or radiotherapy as an alternative.
SYMPTOMS
Gallbladder cancer is difficult to diagnose due to lack of noticeable symptoms present particularly on the early stages of the disease. Then again, when symptoms manifest, warning indicators are often similar with those other common diseases. Therefore, even if there are major complexities in detecting the disease, knowing these possible signs may be of great help:
- Mild to severe pain on top of or on the upper right side the stomach
- Bloating
- Jaundice (this manifest on dominating colors of whites in the eyes and yellowish color of the skin)
- Frequent vomiting and unsettled stomach
- High fever
- Lumps in the abdomen region
- The urine is dark yellow in color
CAUSES
Medical research is yet to discover the causes behind cancer of the gallbladder. However, there are certain risk factors that may contribute in your chances of acquiring this kind of disease.
Inflammation of the gallbladder and formation of gallstones – If you are enduring any of these or have a history of inflammation and gallstones, there is an average chance of having cancer of the gallbladder. Nonetheless, most cases of inflamed gallbladder or those who have developed stones do not automatically obtain this kind of cancer. A list of common risk factors is briefly listed below:
- Abnormalities in the bile duct region – Based on studies, patients who have congenital irregularities in the bile region are likely to have this type of cancer.
- Family history – If it runs in the family, all the members are five times possible of having cancer of the gallbladder.
- Obesity – This is one common cause of almost all cancers. If you are overweight, the risk of this kind of cancer is likely to transpire.
TREATMENT
There are three standard types of treatment for gallbladder cancer:
1. Surgery – This is the most standard treatment of all where tissues around the infected area are removed. Furthermore, a laparoscope is also a surgical tool connected and affixed to a video camera and this will serve as the monitor inside the abdomen. This kind of surgery is very sensitive that tissues on other ports used to insert surgical tools are also removed to prevent spreading of the cancer cells. If there are cases where cancer cells have spread through different regions, there are 3 palliative surgeries done:
- Endoscopic Stent Placement
- Surgical Biliary Bypass
- Percutaneous Transhepatic Biliary Drainage
2. Chemotherapy – There are two kinds of chemotherapy. One is systematic chemotherapy and the other is regional chemotherapy. Systematic chemotherapy is either injected or taken in the form of drugs. Once these forms of medications enter the bloodstream, it targets cancerous cells. Conversely, regional chemotherapy is a kind of procedure where treatment is directly placed in the area or region where most cancer cells are present. Both of these procedures are given depending on the condition and stage of cancer a patient is into.
3. Radiation therapy – There are two kinds of radiation therapy. One is external radiation therapy and the other is internal radiation therapy. The former makes use of a machine while the latter uses radioactive tools both for the purpose of sending radiations in destroying cancer cells.
