Leukemia facts
OVERVIEW
Leukemia is one of the most feared cancers in the world. Cancer, first of all, is the process wherein there are abnormal and sickly cells growing and developing in the body. It can occur in many ways and can affect bodily functions drastically, and one of them is leukemia.
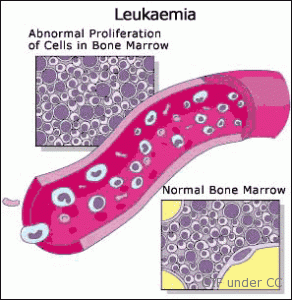
It is basically the immature cells that form within the bone marrow and are accumulated in the blood and in other parts of the body. Doctors who identify blood cells that cannot carry out the normal functions in the body would conclude this as leukemia usually.
To be able to understand leukemia, it is important that you understand the structure and system of the human blood. Normal blood usually contains three major cell groups: white blood cells, red blood cells, and platelets. Each group develops from an immature cell type called the marrow stem cells, which occurs in a process known as hematopoiesis.
The stem cells then divide and grow into more developed cells called blasts, and go through other processes until it becomes a full grown mature blood cell. All this takes place within the bone marrow, which is found in the center or core of most bones in the body.
TYPES AND FORMS:
There are two major types of this disease and two major forms: acute myelocytic, acute lymphocytic, chronic myelocytic and lastly chronic lymphocytic. Acute basically refers to a rapid onset of the cancer while chronic means a slow onset of the cancer, usually in a long time intervals.
- Acute Myelocytic Leukemia – abnormal, immature cells grow and die rapidly. The cells cannot carry out the functions of normal mature white blood cells and when left untreated with chemotherapy and other important treatments will result to death in a matter of weeks or months.
- Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia – abnormal and immature cells are present but instead of growing and dying rapidly, they tend to accumulate in the blood. They still cannot function as normal white blood cells and when left untreated will result to immediate death within weeks or a few months.
- Chronic Myelocytic Leukemia – a more common condition among adults, this type of leukemia has a slow onset wherein the cells grow and eventually die over long time intervals. One of the most distinctive characteristics of this particular chronic leukemia is its conversion into a rapid and acute type of cancer, which of course will lead to a rapid death when left untreated.
- Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia – this type of chronic leukemia, commonly known as an adult disorder and twice as common, has a slow onset and takes long periods of time to grow and accumulate within the blood. This type, along with the chronic myelocytic, when untreated can persist for many months or years.
SYMPTOMS
Leukemia symptoms may vary depending on what type and form they take. For acute types, the symptoms would usually develop quickly while for chronic types, they gradually develop and are not as severe as compared to the former. Usually symptoms are due to major deficiencies of the normal blood cells while others are due to accumulated leukemia cells in the different organs and tissues of the body. But for the sake of summarization, here is a list of some of the major symptoms of acute leukemia:
- Infection
- Sudden fevers
- Fatigue
- Sweating during nighttime
- Weight loss
- Easily bleeds or bruised
This is a list of the major symptoms caused by chronic or accumulated leukemia cells:
- Headaches
- Unexplained confusion
- Blurred vision
- Painful swellings, particularly in the arms, groin, and neck
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea and vomiting
- Abdominal pains and swelling
- Pain in the bones and joints
- Loss of control or weakness in the body muscles
CAUSES
Scientists and doctors have yet to discover the major cause of leukemia, but researchers have found several factors and causes that could have contributed to the development of cancer. Some of the causes, such as exposure to harmful chemicals, radiation, and consistent smoking are usually relative risk factors as some people have developed this disease without such exposures.
Some have also concluded that previous diseases, as well as family history, could also be risk factors that could lead to leukemia.
TREATMENT
It is important that a patient who has the cancer be diagnosed and examined by a specialist known as hematologists or hematologist-oncologists since these people specialize on leukemia cases.
There are basically two stages of treatment: first, the treatment to fight leukemia and second, the treatment to relieve the symptoms caused by this disease. The most widely used treatment for such a cancer is chemotherapy, which is the use of powerful drugs in order to kill the cancer cells.
